class: center, middle, inverse, title-slide # Lab07_Visualizing-Data-Tips ## Lab06_ggplot2-layered-graphics ### 曾子軒 Dennis Tseng ### 台大新聞所 NTU Journalism ### 2021/04/13 --- <style type="text/css"> .remark-slide-content { padding: 1em 1em 1em 1em; font-size: 28px; } .my-one-page-font { padding: 1em 1em 1em 1em; font-size: 20px; /*xaringan::inf_mr()*/ } </style> # 今日重點 - 沒有作業 - 期中個人資料新聞 - AS05 檢討 - `ggplot2` layers - Lab067 Practice --- # 作業檢討 - [Lab06 範例解答](https://p4css.github.io/R4CSS_TA/Lab06_Homework_Visualizing-Date-Time_ref)、[AS05 範例解答](https://p4css.github.io/R4CSS_TA/AS05_Visualizing-Date-Time_ref.html) --- # ggplot2 layer - 組成 - data + `ggplot(aes( ))` + `geom_**()` + ... - 資料層 + 美學層 + 幾何層 + ... <img src="photo/Lab06_ggplot01.jpg" width="55%" height="55%" /> source: [Datacamp - Introduction to Data Visualization with ggplot2](https://www.datacamp.com/courses/data-visualization-with-ggplot2-1) --- # ggplot2 layer - 概念上 - 圖表由 layer + scales + coordinate + facet + theme 所組成 - Layer 負責我們在圖表中看到的物件 - Data - Aesthetic mappings - A statistical transformation (stat) - A geometric object (geom) - A position adjustment --- # ggplot2 layer - 概念上 - 圖表由 layer + scales + coordinate + facet + theme 所組成 - Scales 負責控制變數轉換到美學的mapping - 每個變數都需要一個 scale, e.g. x, y, color, fill, etc. - 分為連續和類別,可以手動補值, e.g. `scale_x_continuous()`, `scale_fill_manual()` - 因為它控制轉換,所以也包含怎麼用圖例和座標軸向讀者解釋 - 用英文比教好懂:Each scale is a function from a region in data space (the domain of the scale) to a region in aesthetic space (the range of the scale). The axis or legend is the inverse function: it allows you to convert visual properties back to data. --- # ggplot2 layer - Scales 負責控制變數轉換到美學的mapping Argument name | Axis | Legend --------------|-------|------ name | Label | Title breaks | Ticks & grid line | Key labels | Tick label | Key label <img src="photo/Lab07_ggplot_guides.png" width="55%" height="55%" /> --- # ggplot2 layer - 概念上 - 圖表由 layer + scales + coordinate + facet + theme 所組成 - Coordinate System 負責把物件位置對應到圖片的平面/表面(plane)上 - 最常見到二維,但也有非直角坐標的像是 polar system - Facet 負責將圖表依照特定變數切分成多格,實用所以拉出來談 - Theme 負責實質資料以外的內容 - 內容非常多樣,舉凡字體、位置、框線等皆屬之 - 有現成套件如 `library(ggthemes)` 可以直接調用 --- # ggplot2 layer - 概念上 - 圖表由 layer + scales + coordinate + facet + theme 所組成 - 實務上 - data: 你要用的資料,可以很多 - aesthetics: 選擇要映射的資料變數、怎麼映射,可以很多 - geometries: 不同類型的圖表, 可以很多 - coordinate: 有沒有要調整座標系統、座標軸 - facet: 有沒有要用到 facet - scale: 資料變數映射過程中如何對應 - legend and axis: 視覺變數如何對應回去資料變數 - title and lab: 標題、次標、註解 - theme: 通常有背景、框線、字體 --- # ggplot2 layer ```r library(tidyverse) diamonds %>% head(5) ``` ``` ## # A tibble: 5 x 10 ## carat cut color clarity depth table price x y z ## <dbl> <ord> <ord> <ord> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> ## 1 0.23 Ideal E SI2 61.5 55 326 3.95 3.98 2.43 ## 2 0.21 Premium E SI1 59.8 61 326 3.89 3.84 2.31 ## 3 0.23 Good E VS1 56.9 65 327 4.05 4.07 2.31 ## 4 0.290 Premium I VS2 62.4 58 334 4.2 4.23 2.63 ## 5 0.31 Good J SI2 63.3 58 335 4.34 4.35 2.75 ``` --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: data & aes .pull-left[ ```r ggplot(data = diamonds) + aes(x = carat, y = price, color = cut) ``` ] .pull-right[ <!-- --> ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: geom .pull-left[ ```r ggplot(data = diamonds) + aes(x = carat, y = price, color = cut) + geom_point() ``` ] .pull-right[ <!-- --> ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: stat .pull-left[ ```r ggplot(data = diamonds) + aes(x = carat, y = price, color = cut) + geom_point() + geom_smooth(se = F) ``` ] .pull-right[ ``` ## `geom_smooth()` using method = 'gam' and formula 'y ~ s(x, bs = "cs")' ``` <!-- --> ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: position adjustment .pull-left[ ```r ggplot(data = diamonds) + aes(x = carat, y = price, color = cut) + geom_point(position = position_jitter( height = 100, width = 0.1)) ``` ] .pull-right[ <!-- --> ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: scale and guides .pull-left[ ```r ggplot(data = diamonds) + aes(x = carat, y = price, color = cut) + geom_point(position = position_jitter(height = 100, width = 0.1)) + scale_color_brewer(name = "cut of diamonds", palette = 1) ``` The brewer scales provides sequential, diverging and qualitative colour schemes from ColorBrewer. ] .pull-right[ <!-- --> ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: scale and guides .pull-left[ ```r ggplot(data = diamonds) + aes(x = carat, y = price, color = cut) + geom_point(position = position_jitter(height = 1), alpha = 0.3) + scale_color_brewer(name = "cut of diamonds", palette = 1) + scale_x_continuous(name = "carat of the diamond") ``` ] .pull-right[ <!-- --> ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: scale and guides .pull-left[ ```r ggplot(data = diamonds) + aes(x = carat, y = price, color = cut) + geom_point(position = position_jitter(height = 1), alpha = 0.3) + scale_color_brewer(name = "cut of diamonds", palette = 1) + scale_x_continuous(name = "carat of the diamond") + scale_y_continuous(name = "price of the diamond", limits = c(0, 22500), breaks = c(2500, 7500, 12500, 17500, 22500), labels = scales::comma) ``` ] .pull-right[ <!-- --> ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: labs .pull-left[ ```r ggplot(data = diamonds) + aes(x = carat, y = price, color = cut) + geom_point(position = position_jitter(height = 1), alpha = 0.3) + scale_color_brewer(name = "cut of diamonds", palette = 1) + scale_x_continuous(name = "carat of the diamond") + scale_y_continuous(name = "price of the diamond", limits = c(0, 22500), breaks = c(2500, 7500, 12500, 17500, 22500), labels = scales::comma) + labs( #x = "carat of the diamond", #y = "price of the diamond", #colour = "cut of the diamond", title = "Price and Carat of Diamonds are Highly Correlated", subtitle = "Cut of diamonds play a part also", caption = "source: library(tidyverse)" ) ``` ] .pull-right[ <!-- --> ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: theme .pull-left[ ```r ggplot(data = diamonds, aes(x = carat, y = price, color = cut)) + geom_point(position = position_jitter(height = 1), alpha = 0.3) + scale_color_brewer(name = "cut of diamonds", palette = 1) + scale_x_continuous(name = "carat of the diamond") + scale_y_continuous(name = "price of the diamond", limits = c(0, 22500), breaks = c(2500, 7500, 12500, 17500, 22500), labels = scales::comma) + labs(title = "Price and Carat of Diamonds are Highly Correlated", subtitle = "Cut of diamonds play a part also", caption = "source: library(tidyverse)") + theme(plot.title = element_text(face = "bold", size = 16), panel.background = element_blank(), legend.background = element_rect(fill = "white", size = 4, colour = "white"), panel.grid.major = element_line(colour = "grey70", size = 0.2)) ``` ] .pull-right[ 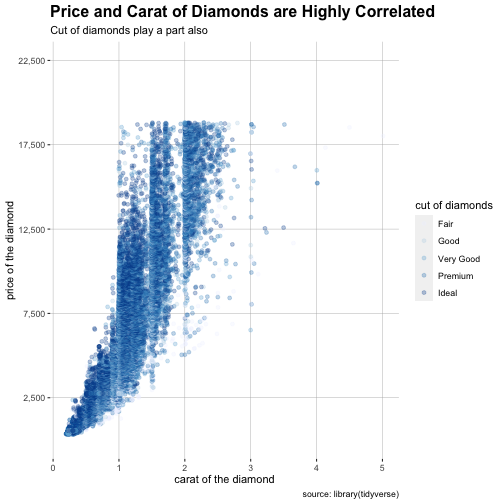<!-- --> ] --- class: inverse, center, middle # 「讓我們從頭開始」 --- # ggplot2 layer - 實務上 - data: 你要用的資料,可以很多 - aesthetics: 選擇要映射的資料變數、怎麼映射,可以很多 - geometries: 不同類型的圖表, 可以很多 - coordinate: 有沒有要調整座標系統、座標軸 - facet: 有沒有要用到 facet - scale: 資料變數映射過程中如何對應 - legend and axis: 視覺變數如何對應回去資料變數 - title and lab: 標題、次標、註解 - theme: 通常有背景、框線、字體 --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: data ``` ## Warning: package 'maps' was built under R version 4.0.2 ``` ``` ## Warning: package 'sf' was built under R version 4.0.2 ``` ```r df_city_taiwan %>% head(2) ``` ``` ## # A tibble: 2 x 6 ## name country.etc pop lat long capital ## <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <int> ## 1 Changhwa Taiwan 227178 24.1 121. 0 ## 2 Chaochou Taiwan 58839 22.6 121. 0 ``` ```r sf_county %>% head(2) ``` ``` ## Simple feature collection with 2 features and 4 fields ## geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON ## dimension: XY ## bbox: xmin: 119.9089 ymin: 24.30943 xmax: 124.5611 ymax: 26.38528 ## geographic CRS: TWD97 ## COUNTYID COUNTYCODE COUNTYNAME COUNTYENG ## 1 Z 09007 連江縣 Lienchiang County ## 2 G 10002 宜蘭縣 Yilan County ## geometry ## 1 MULTIPOLYGON (((119.9645 25... ## 2 MULTIPOLYGON (((121.9597 24... ``` --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: data .pull-left[ ```r sf_county %>% st_crop(xmin=119,xmax=123,ymin=20,ymax=26) %>% ggplot() + geom_sf() + theme_void() ``` ] .pull-right[ ``` ## although coordinates are longitude/latitude, st_intersection assumes that they are planar ``` ``` ## Warning: attribute variables are assumed to be spatially constant throughout all ## geometries ``` <!-- --> ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: data .pull-left[ ```r sf_county %>% st_crop(xmin=119,xmax=123,ymin=20,ymax=26) %>% ggplot() + geom_sf() + geom_point(data=df_city_taiwan, aes(x=long, y=lat)) + theme_void() ``` ] .pull-right[ ``` ## although coordinates are longitude/latitude, st_intersection assumes that they are planar ``` ``` ## Warning: attribute variables are assumed to be spatially constant throughout all ## geometries ``` 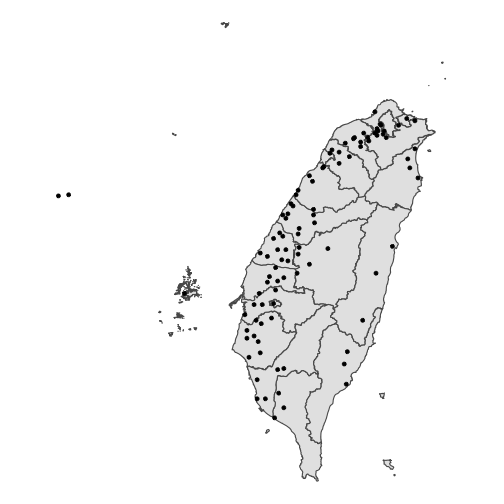<!-- --> ] --- # ggplot2 layer: aesthetics - aesthetics: 選擇要映射的資料變數、怎麼映射,可以很多 - 位置(x / y axis) - 顏色(color) - 大小(size) - 透明程度(alpha) - 填滿(fill) - 形狀(shape) - 注意用變數映射與手動指定的差異 --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: aesthetics .pull-left[ ```r diamonds %>% group_by(cut, color) %>% summarise(price = mean(price), carat = mean(carat)) %>% ungroup() %>% ggplot(aes(x = cut, y = price)) + geom_bar(stat = "identity") ``` ] .pull-right[ ``` ## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'cut'. You can override using the `.groups` argument. ``` 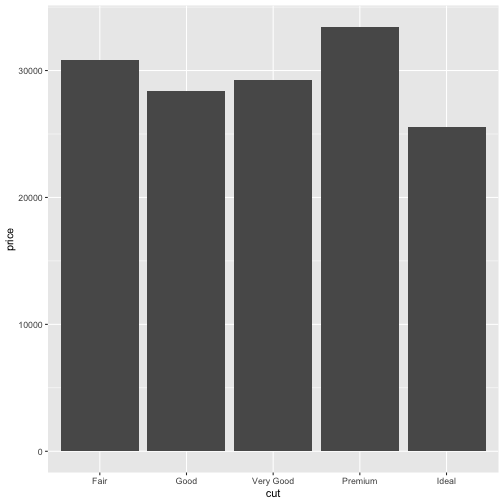<!-- --> ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: aesthetics .pull-left[ ```r diamonds %>% group_by(cut, color) %>% summarise(price = mean(price), carat = mean(carat)) %>% ungroup() %>% ggplot(aes(x = cut, y = price, fill = color)) + geom_bar(stat = "identity") ``` ] .pull-right[ ``` ## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'cut'. You can override using the `.groups` argument. ``` <!-- --> ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: aesthetics .pull-left[ ```r diamonds %>% group_by(cut, color) %>% summarise(price = mean(price), carat = mean(carat)) %>% ungroup() %>% ggplot(aes(x = cut, y = price, alpha = color)) + geom_bar(stat = "identity") ``` ] .pull-right[ ``` ## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'cut'. You can override using the `.groups` argument. ``` <!-- --> ] --- # ggplot2 layer: geometries and statistics - geometries: 不同類型的圖表, 可以很多 - `point/jitter` - `line/path` - `bar/col` - `rect/tile/raster` - `density` - statistics: 不同類型的圖表, 可以很多 - uncertainty: `errorbar/linerange/smooth` - weighted data - distributions: `histogram/freqpoly/boxplot` --- # ggplot2 layer: coordinate - coordinate: 有沒有要調整座標系統、座標軸 - 線性的: `cartesian/flip/fixed` 分別代表笛卡爾坐標系、翻轉、固定 - 非線性的: `sf/polar/trans` 分別代表地圖投影、極性、轉換 --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: coordinate .pull-left[ ```r diamonds %>% ggplot(aes(x = depth, y = table, color = carat)) + geom_point() + coord_fixed() ``` ] .pull-right[ <!-- --> ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: coordinate .pull-left[ ```r diamonds %>% ggplot(aes(x = carat, y = price)) + geom_point() ``` ] .pull-right[ ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: coordinate .pull-left[ ```r diamonds %>% ggplot(aes(x = carat, y = price)) + geom_point() + coord_trans(y = "log10") ``` ] .pull-right[ <!-- --> ] --- # ggplot2 layer: facet - facet: 有沒有要用到 facet - 用來分層的 `grid/wrap`,以`facet_wrap()`為例子 - x ~ y 用來放想要看得變數 - nrow, ncol 用來擺放列行數量 - scales 可以選`fixed`(固定), `free`(完全沒限制), `free_x/y`(只限制特定座標軸) --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: facet .pull-left[ ```r diamonds %>% ggplot(aes(x = carat, y = price)) + geom_point() ``` ] .pull-right[ <!-- --> ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: facet .pull-left[ ```r diamonds %>% ggplot(aes(x = carat, y = price)) + geom_point() + facet_wrap(clarity ~ .) ``` ] .pull-right[ <!-- --> ] --- class: my-one-page-font # ggplot2 layer: facet .pull-left[ ```r diamonds %>% ggplot(aes(x = carat, y = price)) + geom_point() + facet_wrap(clarity ~ ., scales = "free") ``` ] .pull-right[ <!-- --> ] --- # ggplot2 layer: scale, and guides - scale: 資料變數映射過程中如何對應 - 不連續/連續: `scale_x_discrete()/scale_x_continous()` or y - 不連續/連續: `scale_fill_discrete()/scale_fill_continous()` or color - 不連續/連續: `scale_fill_brewer()/scale_fill_gradient()` or color - 有時候需要手動: `scale_fill_manual()` or color - 參數很多,`breaks`, `labels`, `limits` 是最常用到的,有很多方法可以做到同一件事 - guides(legend and axis): 視覺變數如何對應回去資料變數 - 在裡面放 scale 對應的變數 - 可以放名字,也可以手動改 label --- # ggplot2 layer: scale, and guides - title and lab: 標題、次標、註解 - 同樣有很多方法可以做到同一件事 - theme: 通常有背景、框線、字體 - 非常細節,通常有興趣才會研究,直接來練習看看! --- class: inverse, center, middle # [Lab07](https://p4css.github.io/R4CSS_TA/Lab07_Homework_Visualizing-Data-Tips.html)